
What is a digital product?
| English | Polish |
|---|---|
The digital age shifted the definition of modern day products. Traditionally, products were the results of craftsmen. After the Industrial Revolution, craftsmen and inventors used the manufacturing process to design, produce, and sell their goods at scale. The discipline of “product design” was born from this movement to deliver beautiful and useful products to people that otherwise may not be able to afford them. Since then, product design has evolved drastically. | Era cyfrowa zmieniła definicję współczesnych produktów. Tradycyjnie, produkty były wynikiem pracy rzemieślników. Po rewolucji przemysłowej, rzemieślnicy i wynalazcy wykorzystywali proces produkcyjny do projektowania, produkcji i sprzedaży swoich wyrobów na dużą skalę. Z tego ruchu zrodziła się dyscyplina „projektowanie produktów”, aby dostarczać piękne i użyteczne produkty ludziom, których inaczej nie byłoby na nie stać. Od tego czasu projektowanie produktów bardzo się rozwinęło. |
In the digital age, the term “product” encompasses both hardware and software. Goods and services are no longer solely physical goods, but experiences that users have in the physical world, on a screen, or a mixture between the two. They aim to solve a pain point in people’s everyday lives. | W erze cyfrowej termin „produkt” obejmuje zarówno sprzęt, jak i oprogramowanie. Towary i usługi nie są już wyłącznie towarami fizycznymi, ale wrażeniami (doświadczeniami), które użytkownicy odbierają w świecie fizycznym, na ekranie lub z połączenia jednego i drugiego. Mają one na celu rozwiązywanie problemów ludzi w ich życiu codziennym. |
For example, a notebook has physical design aspects: It can be made of different materials, paper, and bindings. However, the end goal of a physical notebook — the capability it aims to give you — is similar to digital tools such as Google Docs or Microsoft Word. These digital products are made up of different interactions, styles, and code, creating a completely different user experience, but they solve similar user needs to a physical notebook. | Na przykład, notes ma fizyczne cechy konstrukcyjne: może być wykonany z różnych materiałów, papieru i opraw. Jednak ostateczny cel fizycznego notesu – możliwości, jakie oferuje – jest podobny do narzędzi cyfrowych, takich jak Google Docs czy Microsoft Word. Te produkty cyfrowe składają się z różnych interakcji, stylów i kodu, tworząc zupełnie inne wrażenia użytkownika, ale zaspokajają podobne potrzeby jak fizyczny notes. |

What is a product design?
| English | Polish |
|---|---|
Product design is the whole product experience. It’s an amorphous phrase, and flavors and processes for product design vary widely. It could mean designing a mobile app, a web app, a website, a dashboard, branding, or all of the above. | Projektowanie produktu to całe doświadczenie związane z produktem. Jest to wyrażenie amorficzne, a cechy i procesy projektowania produktu są bardzo zróżnicowane. Może to oznaczać projektowanie aplikacji mobilnej, aplikacji internetowej, strony internetowej, panelu użytkownika, brandingu lub wszystkich powyższych. |
An unfortunate misconception is that product design exists to make products look pretty. In reality, it’s a product designer’s responsibility to curate a consistent end-to-end experience for users using research, product strategy, and a visual language consistent with a company’s brand. | Niefortunnym nieporozumieniem jest przekonanie, że projektowanie produktu istnieje po to, aby nadać mu ładny wygląd. W rzeczywistości obowiązkiem projektanta produktu jest zapewnienie użytkownikom spójnego, całościowego wrażenia dzięki badaniom, strategii produktu i wizualnego języka spójnego z marką firmy. |
Now that you have the right background, let’s jump back into a more thorough description of what product design entails. Product design is a discipline that solves problems fast and holistically. It’s a method of creating, iterating, and testing your solutions to make the user’s experience better. | Teraz, gdy masz już odpowiedni kontekst, wróćmy do dokładniejszego opisu tego, co wiąże się z projektowaniem produktu. Projektowanie produktu to dyscyplina, która szybko i holistycznie rozwiązuje problemy. Jest to metoda tworzenia, iteracji i testowania rozwiązań, aby poprawić wrażenia użytkownika. |
It’s the product designer’s responsibility to make sure that the user has good experience across the entire product. As Steve Jobs said, “Design is not just what it looks and feels like. Design is how it works.” | Obowiązkiem projektanta produktu jest dopilnowanie, aby użytkownik odniósł pozytywne wrażenia z całego użytkowania produktu. Jak powiedział Steve Jobs: „Design to nie tylko wygląd i wrażenia, ale także sposób, w jaki coś działa”. |
With holistic product design, you take a company’s branding and weave its voice, tone, visuals, and values throughout the product. It involves consistent interactions that the user can relate to; at the same time, it uses a design system to make software engineers’ lives easier. It means taking user research into a company leadership meeting and speaking on behalf of their needs to guide the road map. | Dzięki holistycznemu projektowaniu produktu bierzesz markę firmy i wplatasz jej głos, ton, wygląd i wartości w cały produkt. Wiąże się to ze spójną interakcją, którą użytkownik będzie mógł zrozumieć; jednocześnie wykorzystuje się system projektowania do ułatwienia życia inżynierom oprogramowania. Oznacza to przedstawienie badań użytkowników na spotkaniu kierownictwa firmy i wypowiedzenie się na temat ich potrzeb, aby ukierunkować plan działania. |
What is design thinking?
| English | Polish |
|---|---|
A designer’s loose road map to creating products is through what we call “the design process”, which takes advantage of design thinking. | Luźny plan działania projektanta ukierunkowany na tworzenie produktów jest realizowany za pomocą tego, co nazywamy „procesem projektowania”, który wykorzystuje myślenie projektowe. |
Design thinking has long been considered the holy grail of innovation — and the remedy to stagnation. It has been credited with remarkable feats, like transforming Airbnb from a failing startup to a billion-dollar business. It’s a concept that’s becoming increasingly hard to ignore, and yet, despite such high-profile success stories, it’s a concept that continues to be shrouded in mystery. The famous inventor, engineer, businessman, and holder of no fewer than 186 patents Charles Kettering once said, “If you have always done it that way, it is probably wrong.” | Myślenie projektowe od dawna uważane jest za Świętego Graala innowacji i remedium na stagnację. Przypisano mu niezwykłe rezultaty, takie jak przekształcenie Airbnb z upadającego startupu w biznes wart miliardy dolarów. Jest to koncepcja, którą coraz trudniej zignorować, a mimo tak głośnych sukcesów, jest to koncepcja, która wciąż owiana jest tajemnicą. Słynny wynalazca, inżynier, biznesmen i posiadacz ponad 186 patentów, Charles Kettering powiedział kiedyś: „Jeśli zawsze robiłeś to w ten sposób, to prawdopodobnie robisz to źle”. |
Design thinking is both an ideology and a process that seeks to solve complex problems in a user-centric way. It focuses on achieving practical results and solutions that are: | Myślenie projektowe jest zarówno ideologią, jak i procesem, który ma na celu rozwiązywanie złożonych problemów w sposób zorientowany na użytkownika. Koncentruje się na osiąganiu praktycznych rezultatów i rozwiązań, które są: |
Technically feasible: They can be developed into functional products or processes; Economically viable: The business can afford to implement them; Desirable for the user: They meet a real human need. | Technicznie wykonalne: mogą zostać rozwinięte w funkcjonalne produkty lub procesy; Ekonomicznie opłacalne: przedsiębiorstwo może sobie pozwolić na ich wdrożenie; Pożądane dla użytkownika: zaspokajają realną potrzebę ludzką. |
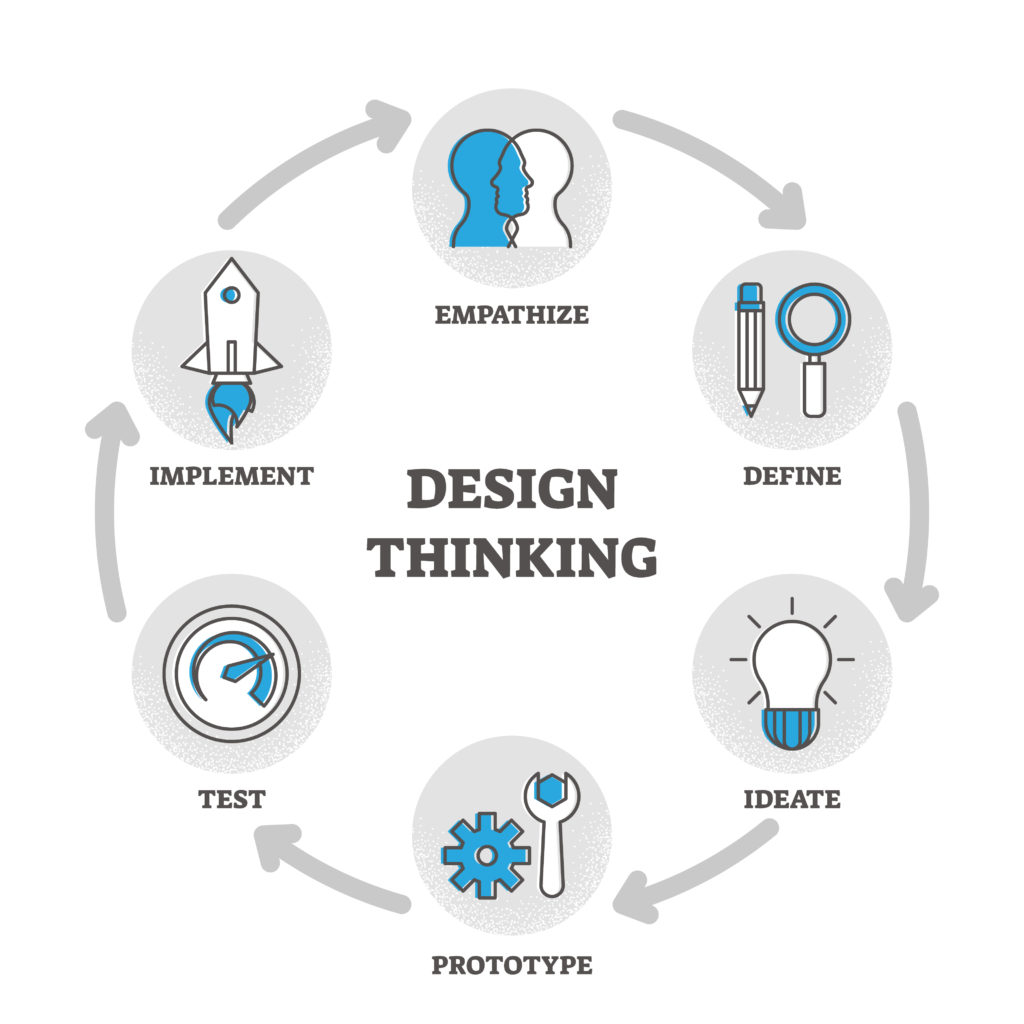
The design thinking framework can be divided into three distinct phases: immersion, ideation, and implementation. This framework can be further broken down into five actionable steps which make up the design thinking process: 1. Empathize 2. Define 3. Ideate 4. Prototype 5. Test | Schemat myślenia projektowego można podzielić na trzy odrębne fazy: zanurzenie, generowanie pomysłów i realizację. Schemat ten można dalej podzielić na pięć wykonalnych kroków, które składają się na proces myślenia projektowego: 1. Empatyzacja 2. Definiowanie problemu 3. Generowanie pomysłów 4. Tworzenie prototypów 5. Testowanie |
Although these steps appear to be sequential, it’s important to point out that design thinking doesn’t follow a strictly linear process. At each stage in the process, you’re likely to make new discoveries that require you to go back and repeat a previous step. | Mimo że te kroki wydają się sekwencyjne, ważne jest, aby zwrócić uwagę na fakt, że myślenie projektowe nie podąża według ściśle liniowego procesu. Na każdym jego etapie prawdopodobnie dokonasz nowych odkryć, które wymagają cofnięcia się i powtórzenia poprzedniego kroku. |
Source of English text: https://www.invisionapp.com/design-defined/product-design/
Exercises:
Exercise 1.
Answer the questions.
- How was the discipline of 'product design’ born?
- What does the term ‘product’ encompass”?
- What is product design?
- What is a misconception about product design?
- How could you describe a holistic approach to product design?
- What is the product designer’s responsibility?
- What has been considered the holy grail of innovation?
- What is design thinking?
- What should the practical results and solutions of design thinking be?
- What are the five steps of the design thinking process?
Exercise 2.
Exercise 3.
Exercise 4.
Exercise 5.